maemo SDK+ Control Panel Applets
This document explains how to install and set up the maemo SDK+ extra Control Panel Applets for your tablet. These tools are useful for developers who wish to setup USB Networking between their Internet Tablet and development host Linux machine, or control the runtime system services, such as syslog and sbrsh. This document is targeted for maemo application developers. The tools described in this document are meant to be used by experienced software developers only.
Click on the install link on the tablet to install the applets using the Application Manager. This will install maemo-control-usb and maemo-control-services packages on the Internet Tablet, providing Control Panel Applets for USB Networking and Services.
These tools will appear in Extras section of the control panel:

USB Networking applet
By default, the USB connection provides USB mass storage access to the memory card. The control panel applet USB Networking allows to change to USB networking mode.
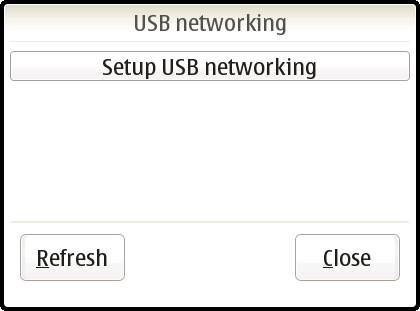
Tap on Setup USB Networking -button to start USB networking. This will do the following:
- Test if USB interface is in use.
- Inserts g_ether kernel module which provides Ethernet over USB networking. The kernel driver will make the device appear as Netchip Technology, Inc. Linux-USB Ethernet/RNDIS Gadget to USB host. Run lsusb command on the host to see if the driver is found.
- Runs ifup usb0 to start usb0 networking interface.
The applet has a few known problems:
- Does not support changing back to file storage mode. File storage mode is available after rebooting the tablet.
- When USB networking is in use, USB cable disconnections are not properly detected by Linux HAL.
- Any memory card mounts are unmounted while USB cable connection is detected, also when in USB networking mode. Might require the changing of ke-recv scripts: /usr/sbin/osso-usb-mass-storage-{enable,disable,is-used}.sh .
- Sometimes after changing to USB Networking mode the Internet Tablet is not visible with lsusb on the other end until the device is rebooted.
- Does not integrate with Internet Connectivity Daemon, other than providing a dummy entry.
- Not possible to use USB networking with Hildon applications that use Internet Connectivity, such as browser, due to missing name resoving. USB networking uses static IP address and cannot have information about DNS, except when manually configured, thus DNS name resolving doesn't work.
- Multiple default routes might appear in the routing table if many networking connections are in place.
This package uses the script /usr/sbin/usb-helper on the background, which you can invoke from command line to change between USB networking, file storage and host mode profiles. It also has the additional feature of changing in to USB host mode. This helper script is setup to run with sudo.
Tablet configuration
The applet is configured to use static IP address 192.168.2.15 for the tablet and 192.168.2.14 for the host. These IP addresses are also used in this document. If you wish to change the setting, edit the file /etc/network/interfaces on the tablet.
Host configuration
Add the following entry to the /etc/network/interfaces file of the host Debian machine:
mapping hotplug
script grep
map usb0
auto usb0
iface usb0 inet static
address 192.168.2.14
netmask 255.255.255.0
network 192.168.2.0
broadcast 192.168.2.255
up iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o eth0 -s 192.168.2.15 -j MASQUERADE
up echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
down iptables -t nat -D POSTROUTING -o eth0 -s 192.168.2.15 -j MASQUERADE
down echo 0 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
Sometimes the networking interface isn't started automatically. To restart the interface, try running ifdown usb0 ; ifup usb0 on the host.
Testing Connection
After making the preparations, the USB network should automatically be set up when connecting the device to the host machine with a USB cable.
For basic testing, pinging can be performed from the host machine:
$ ping 192.168.2.15 PING 192.168.2.15 (192.168.2.15) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 192.168.2.15: icmp_seq=1 ttl=245 time=79.8 ms ...
Services applet
The Services applet can be used to control starting and stopping system init scripts, or change if they are started during system boot. It uses invoke-rc.d for starting and stopping services and update-rc.d for controlling runlevel options. Mark the checkbox next to a service to make it start it during system init. Tap on Running toggle button to start or stop a service. Changed service state should be reflected in the UI.
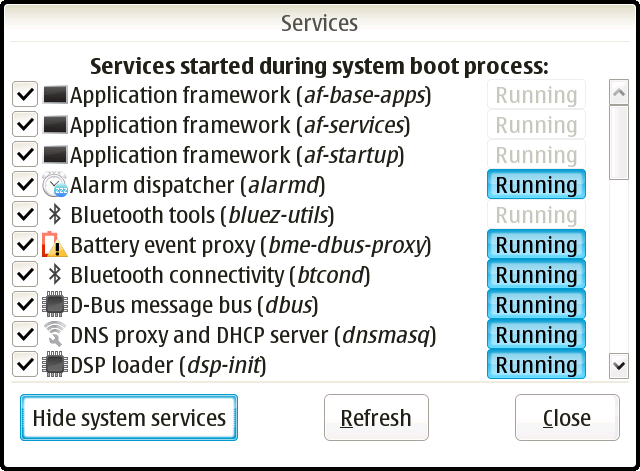
By default, the system services are hidden. Tap on the Hide system services toggle button to show system services. Warning: Stopping system services or removing them from system boot process can affect your system's stability or make your device unusable. Please know what you are doing!
Links
- Parts based on maemo.org HOWTO: Setting up USB networking
- Maemo Service Handler services control panel applet for maemo 3.x Bora
